How to Prevent Jigger Digging: A Practical Guide to Protection and Hygiene
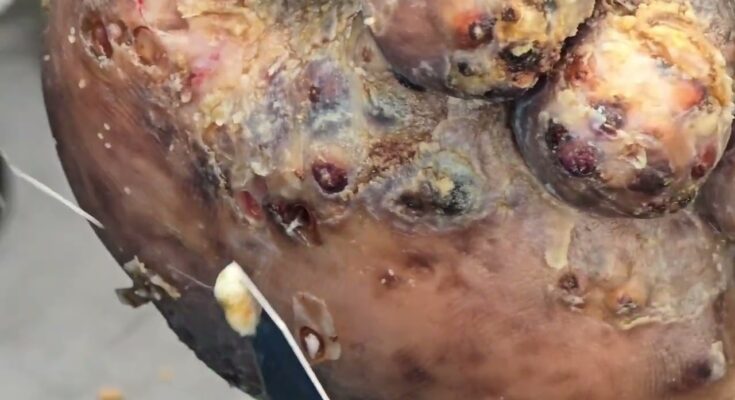
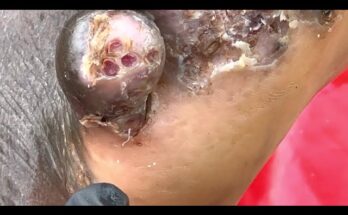
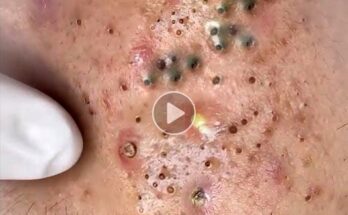
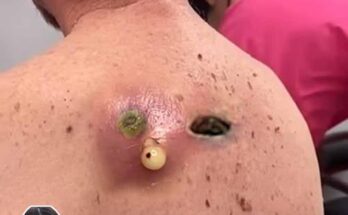
Jiggers, scientifically known as Tunga penetrans, are tiny parasitic fleas that burrow into human skin—most commonly in the feet—causing intense itching, pain, swelling, and in severe cases, secondary infections. This condition, called tungiasis, is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in sandy environments like beaches, farms, and rural villages.
Understanding the Threat
Jiggers thrive in warm, dusty areas and often affect people who walk barefoot or live in unsanitary conditions. Once a female flea penetrates the skin, it lays eggs and causes inflammation, discomfort, and potential disability if untreated. The infestation can become severe when multiple fleas burrow into the skin, leading to difficulty walking and social stigma.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing jigger infestations is straightforward and relies heavily on hygiene, protective clothing, and environmental care:
- 🧼 Foot Hygiene: Wash feet daily with soap and clean water. Trim toenails regularly to reduce hiding spots for fleas.
- 👟 Protective Footwear: Always wear closed-toe shoes or sandals, especially in high-risk areas. This simple habit drastically reduces exposure.
- 🧴 Use Insect Repellent: Applying repellent to feet and legs can deter fleas from approaching the skin.
- 🧹 Clean Living Spaces: Sweep and sanitize floors, especially in homes with earthen surfaces. Avoid clutter and maintain dry, clean environments.
- 🛏️ Sleep Protection: Use clean bedding and avoid sleeping directly on the ground.
- 🧽 Community Cleanups: Participate in or organize local sanitation efforts to reduce flea breeding grounds.
Treatment Tips
If infestation occurs, early treatment is crucial:
- 🛁 Soak affected areas in antiseptic solutions like potassium permanganate to kill embedded fleas.
- 🧴 Apply petroleum jelly or antibiotic ointments to promote healing.
- 🏥 Seek medical help for severe cases to prevent complications like tetanus or gangrene.
Community Awareness
Education is key. Raising awareness about jigger prevention through schools, health campaigns, and local leaders helps reduce stigma and encourages proactive hygiene. In regions where jiggers are endemic, community-wide interventions—like distributing shoes and improving sanitation—have shown significant success.