Treatment and Prevention of Jigger Infestation: A Path to Healing and Protection
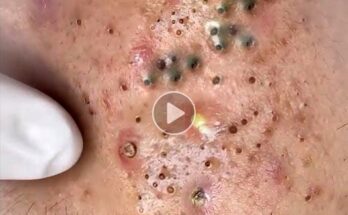
Jigger infestation—medically known as tungiasis—is caused by the parasitic flea Tunga penetrans, which burrows into human skin, typically on the feet and toes. Though tiny, jiggers can cause intense pain, inflammation, and serious complications if left untreated. Effective treatment and prevention are essential to break the cycle of suffering, especially in vulnerable communities.
🩺 Treatment Options for Jigger Infestation
Treating jiggers involves removing the embedded flea, managing symptoms, and preventing infection. Key approaches include:
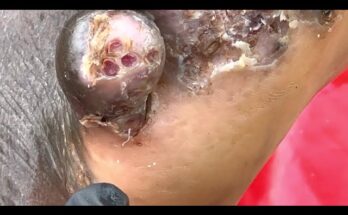
1. Manual Removal
- Clean the affected area with soap and water
- Use sterilized tools (tweezers or needles) to gently extract the flea
- Avoid breaking the flea during removal to prevent further irritation
- Apply antiseptic ointment afterward to reduce inflammation and risk of infection
2. Topical Medications
- Corticosteroid creams to reduce swelling and itching
- Aloe vera gel for soothing irritated skin
- Antihistamine creams to control allergic reactions
3. Oral Medications
- Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen for discomfort
- Antibiotics (topical or oral) for secondary bacterial infections
- Tetanus vaccination if the wound is deep or contaminated
4. Post-Treatment Care
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Monitor for signs of infection
- Complete any prescribed medication courses
- Schedule follow-up care if needed
🛡️ Prevention Strategies
Preventing jigger infestation is more effective and less painful than treating it. Prevention focuses on hygiene, environmental control, and protective behaviors:
1. Footwear and Clothing
- Wear closed-toe shoes, especially in dusty or sandy environments
- Avoid walking barefoot in endemic regions
2. Environmental Improvements
- Replace dirt floors with cement to eliminate breeding grounds
- Use insecticides in homes and animal shelters
- Maintain clean living conditions and reduce overcrowding
3. Hygiene Practices
- Wash feet daily with soap and water
- Keep nails trimmed and clean
- Treat pets and livestock that may carry fleas
4. Community Education
- Raise awareness about jigger symptoms and risks
- Encourage early treatment and discourage stigma
- Train local health workers in safe removal techniques
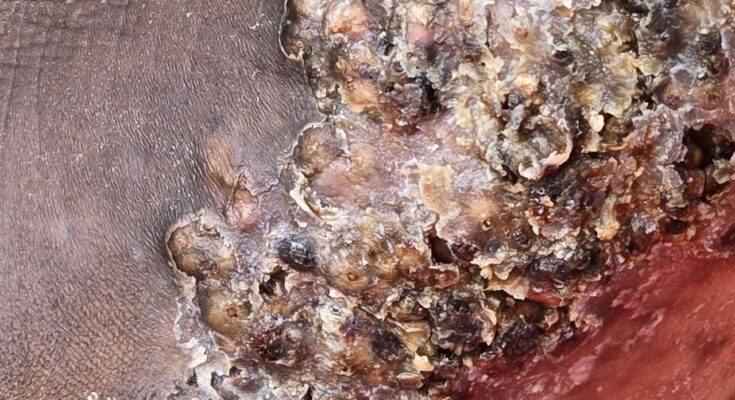
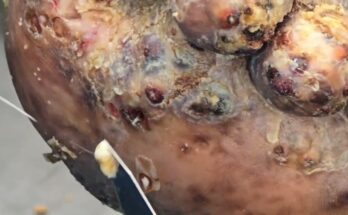
⚠️ Complications to Avoid
If untreated, jigger infestations can lead to:
- Severe pain and difficulty walking
- Nail deformation and tissue damage
- Tetanus, gangrene, or permanent disability
- Social isolation and emotional trauma
Welcome to CasinoTorero.info — the ultimate portal for online casinos!
Need secure gaming platforms?
At casinotorero.info, you’ll get access to expert opinions on new and classic casinos.
Enjoy many casino games, table games, and new releases.
Claim lucrative promotions and start your journey today!
Easy to use: navigate by rating, read helpful tips, and start playing right away.
Sign up at Casino Toreto — where luck meets expertise!
Enjoy and win big!